Dosing
ULTOMIRIS® provides adult patients with predictable, once-every-8-week maintenance dosing for lasting symptom control1,2,a
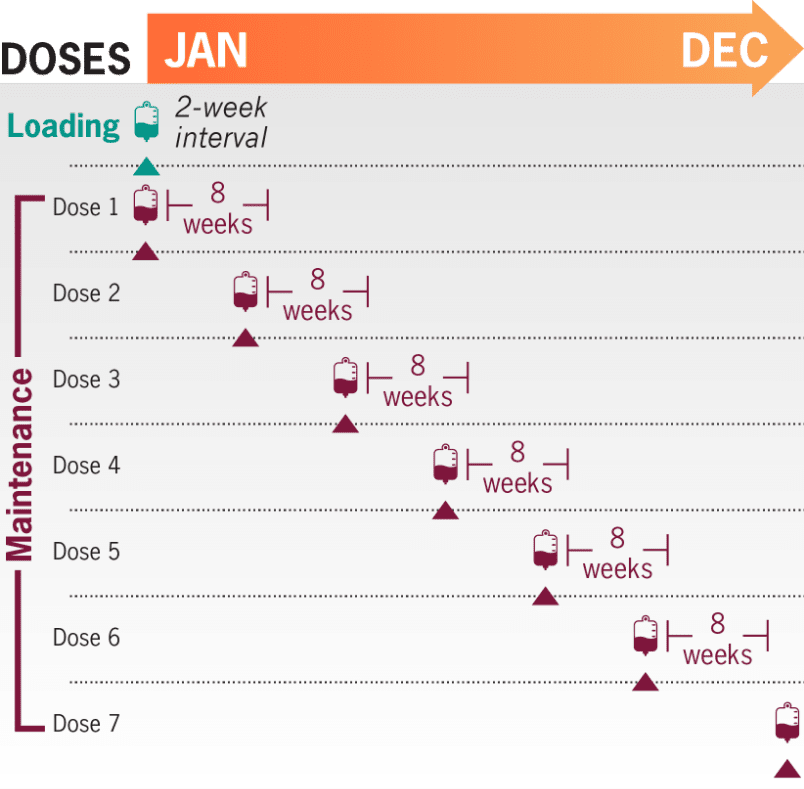
1 infusion every 8 weeksa; 6-7 maintenance infusions per year after a loading dose1
Each infusion typically lasts less than 1 hour for the majority of patients. Patients are monitored for at least 1 hour after infusions for signs or symptoms of an infusion-related reaction1,b
- If an adverse reaction occurs during the administration of ULTOMIRIS (ravulizumab-cwvz), the infusion may be slowed or stopped at the discretion of the physician1
- The recommended weight-based dosing regimen in adult patients with gMG (≥40 kg [88 lb]) consists of a loading dose followed 2 weeks later by the start of maintenance dosing every 8 weeks1
- The dosing schedule is allowed to occasionally vary within 7 days of the scheduled infusion day (except for the first maintenance dose of ULTOMIRIS), but subsequent doses should be administered according to the original schedule1
- Following a missed intravenous ULTOMIRIS dose, the patient should contact their healthcare provider immediately1
aStarting 2 weeks after initial loading dose.1
bMinimum infusion time for ULTOMIRIS 100 mg/mL maintenance doses ranges from 30 minutes to less than 1 hour, depending on body weight.1
Looking for an infusion location for your patient?
Find an Infusion LocationDoses and infusion times for ULTOMIRIS 100 mg/mL1
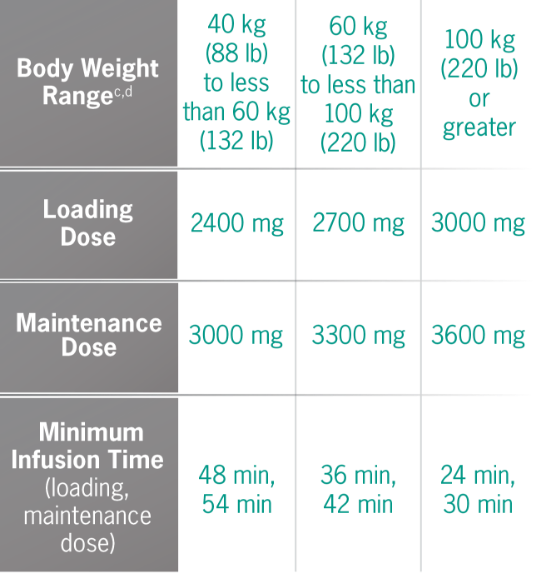
cBody weight at time of treatment.1
dApproximate weight in pounds was calculated using standard weight conversion of 1 kg=2.205 lb.
If an adverse reaction occurs during the administration of ULTOMIRIS, the infusion may be slowed or stopped at the discretion of the physician. Monitor the patient for at least 1 hour following completion of the infusion for signs or symptoms of an infusion-related reaction.1
ULTOMIRIS Dosing Calculator
This calculator tool is for reference only. See the full dosing chart above and the recommended weight-based dosing regimen for gMG in section 2.6 of the ULTOMIRIS Prescribing Information.
Units
Loading dose (mg)
Maintenance dose (mg)
100 mg/mL formulation loading dose vials
100 mg/mL formulation maintenance dose vials
ULTOMIRIS 100 mg/mL dosing at a glance1
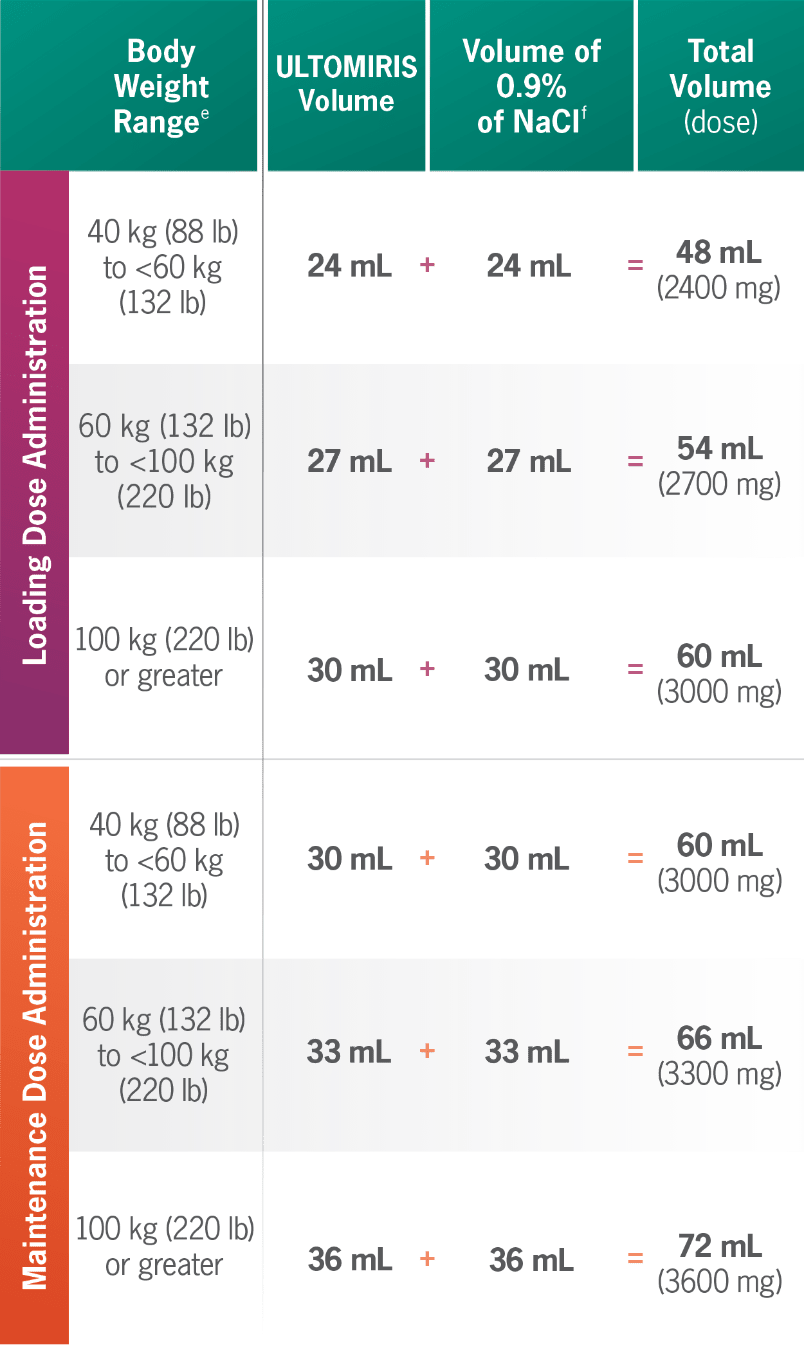
eBody weight at time of treatment.1
fDilute ULTOMIRIS only using 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.1
gMinimum infusion time for ULTOMIRIS 100 mg/mL maintenance doses ranges from 30 minutes to less than 1 hour, depending on body weight.1
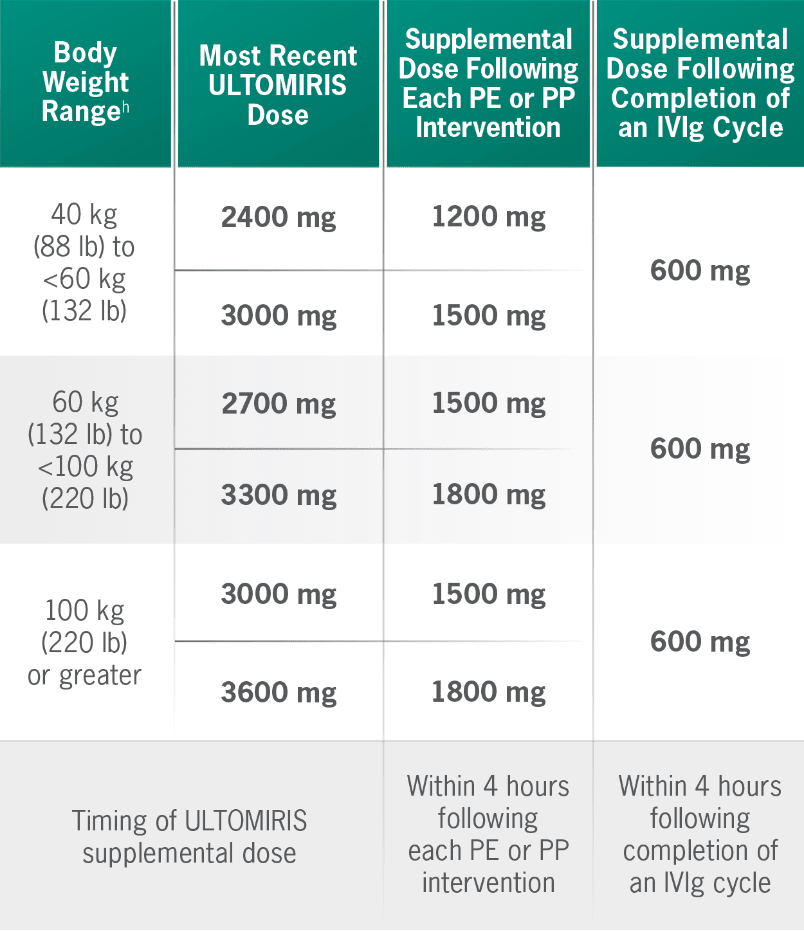
Supplemental dosing of ULTOMIRIS after PE, PP, or IVIg1
Concomitant use of ULTOMIRIS with PE, PP, or IVIg treatment can reduce serum ULTOMIRIS concentrations and requires a supplemental dose of ULTOMIRIS.
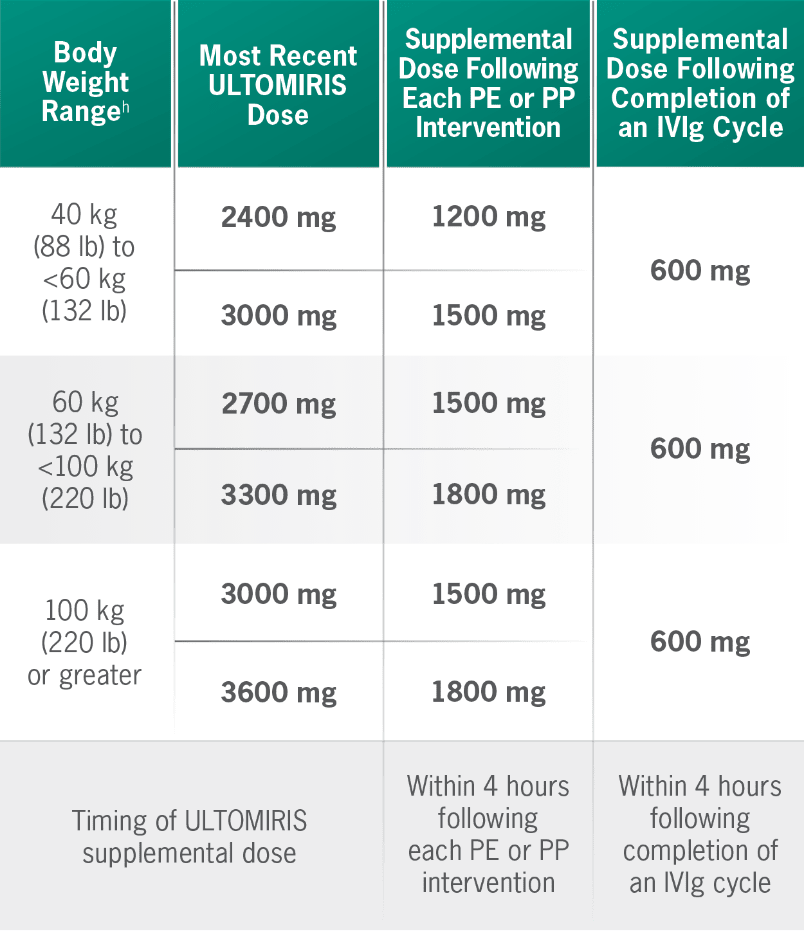
hBody weight at time of treatment.1
Neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) blockers
Concomitant use of ULTOMIRIS with FcRn blockers (eg, efgartigimod) may lower systemic exposures and reduce the effectiveness of ULTOMIRIS. Closely monitor for reduced effectiveness.1
With a predictable, patient-friendly infusion schedule, ULTOMIRIS decreases the treatment burden for adult patients with gMG who are anti-AChR antibody positive. ULTOMIRIS offers the only once-every-8-week maintenance dosing schedule1
AChR, acetylcholine receptor; gMG, generalized myasthenia gravis; IVIg, intravenous immunoglobulin; NaCl, sodium chloride; PE, plasma exchange; PP, plasmapheresis; USP, United States Pharmacopeia.
Images are not of actual patients.